Introduction:
In the intricate landscape of electrical engineering, the alphanumeric codes adorning electrical cables are not arbitrary symbols; they are a precise language that communicates the technical details defining the characteristics of each cable. The alphanumeric code employed for cables adheres to a standardized nomenclature, where each letter or combination represents a specific characteristic of the cable. This standardization ensures consistency and adherence to specifications, fostering reliability and uniformity in the electrical industry. This blog endeavors to decode this alphanumeric tapestry, expanding each abbreviation to unravel the specifications aligned with the IS 7098 (Part 1): 1988 standard.
Decoding the Alphanumeric Code:
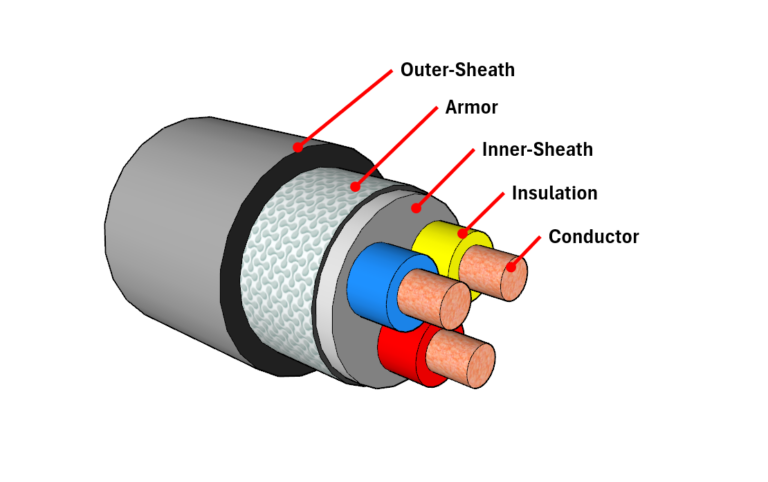
A – Aluminium:
The letter ‘A’ stands for Aluminium, designating this material as the conductor. Aluminium, known for its conductivity and lightweight properties, is widely utilized in cable construction.
2X – XLPE Insulation:
‘2X’ expands to XLPE, signifying Cross-Linked Polyethylene as the insulation material. XLPE is a thermosetting polymer chosen for its superior electrical properties.
W – Steel Round Wire Armour:
The ‘W’ code indicates Steel Round Wire Armour, imparting robust mechanical protection to the cable against external forces.
F – Steel Strip Armour:
‘F’ represents Steel Strip Armour, an alternative form of mechanical reinforcement that enhances the cable’s durability.
WW – Double Steel Round Armour:
‘WW’ denotes Double Steel Round Armour, indicating the presence of two layers of steel round wire armour for heightened protective capabilities.
FF – Double Steel Strip Armour:
Similar to ‘WW,’ ‘FF’ signifies Double Steel Strip Armour, featuring dual layers of steel strip armour for enhanced shielding.
Y – PVC Outer Sheath:
The ‘Y’ code points to the PVC Outer Sheath, which provides an additional layer of insulation and protection to the cable.
Wa – Non-Magnetic Round Wire Armour:
‘Wa’ introduces Non-Magnetic Round Wire Armour, a specialized feature tailored for applications where magnetic properties are a concern.
Fa – Non-Magnetic Strip Armour:
Similarly, ‘Fa’ stands for Non-Magnetic Strip Armour, presenting an alternative form of non-magnetic protection in cable construction.
AW – Aluminum Wire Armour:
‘AW’ indicates the use of Aluminum Wire Armour, offering an alternative to steel for mechanical reinforcement, particularly suitable for specific applications.
Examples:
A2XFaY: Enhanced Resistance
• Conductor Material (A): Aluminum serves as the conductor material.
• Insulation Type (2X): The cable is insulated with Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE).
• Armor Type (Fa): The cable features Non-Magnetic Strip Armor, providing improved resistance.
• Outer Sheath (Y): The outer sheath is composed of PVC.
A2XWWY: Enhanced Protection
• Conductor Material (A): The cable utilizes an Aluminum conductor.
• Insulation Type (2X): Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) is chosen for insulation.
• Armor Type (WW): The cable boasts Double Steel Round Wire Armor, providing robust mechanical reinforcement.
• Outer Sheath (Y): The outer sheath is composed of PVC.
A2XWY: Enhanced Flexibility
• Conductor Material (A): Aluminum is the chosen conductor material.
• Insulation Type (2X): The cable features Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) insulation.
• Armor Type (W): Steel Round Wire Armor provides mechanical reinforcement.
• Outer Sheath (Y): The cable has an outer sheath made of PVC.
Conclusion:
This understanding is not merely theoretical but serves as a strategic tool for professionals in the electrical engineering domain. By decoding these codes in alignment with IS 7098 (Part 1): 1988, professionals can make informed decisions, selecting cables tailored to specific applications. In essence, decoding the alphanumeric tapestry is more than a technical exercise; it’s a key to unlocking the reliability and efficiency of the cables that power our connected world.
